Subsections of MidiInOut parts
Arpeggiator
description
An Arpeggiator plays notes of a chord individually in a progressive rising or descending order.
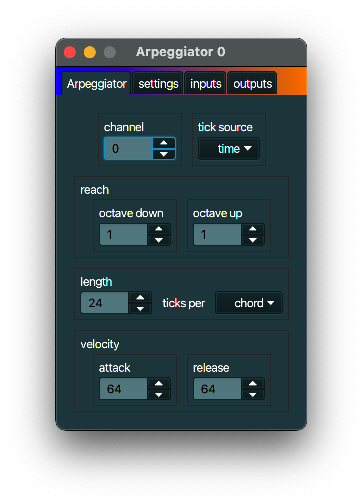

typical use case
Arpeggiators are used in music creation to create a stream of notes, based on chords and
often spanning multiple octaves.
example
Create a MIDI device link and link it to the Gervill software synth. Link your MIDI
keyboard to your computer. Create a MIDI device link and link it to your keyboard. Create an
Arpeggiator and let it get its input from the MIDI keyboard and send its output to
MIDI device link that is linked to the Gervill synth. PLay a chord on your MIDI keyboard. You will
hear the chord notes arpeggiated.
Channel matrix
description
A Channel matrix can redirect all MIDI messages from zero or more MIDI input channels to zero or
more output channels.
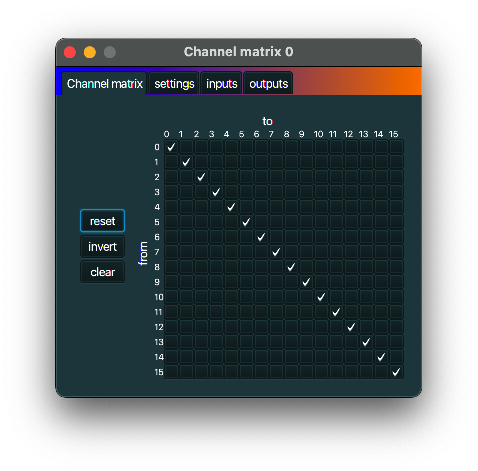

typical use case
If you want to redirect all MIDI messages coming in on channel 0 to instead be send to channel 1
(or to both channel 1 and channel 2), you can use a Channel matrix.
Echo
description
An Echo can replay notes after a specified delay and with a softer velocity.
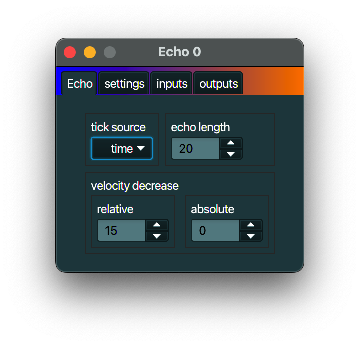

notes
The time between echoed notes is a certain period. That period can be defined relative to the actual
time defined by the (computer) clock, or it can be defined by the number of MIDI clock messages. To
use the latter you must make sure that such MIDI clock messages are actually received by this
MidiInOut, for instance by adding a MIDI clock upstream.
typical use case
I hope you can fill this one yourself.
example
Connect an Echo to the outputs of a Keyboard MIDI keyboard to have an echo-like effect on the
notes played. Note the ’echo-like’, because most synths will only play one note of a certain sound
and the same pitch at a time, instead of overlapping those with different velocities.
Layer and split
description
A Layer and split can map ranges of keys of one channel to other ranges and channels,
while optionally transposing those keys up or down. You have the availability over a virtually
unlimited number of zones. Zones can overlap as well.
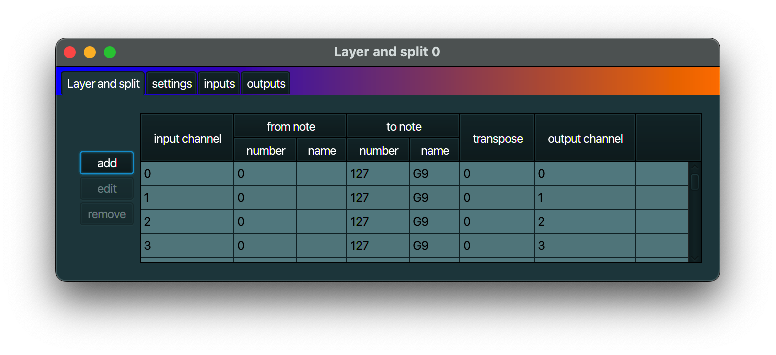

typical use case
If you have an external MIDI keyboard without build-in splitting functionality, you can use a
Layer and split to send keys from one part of your keyboard to one synthesizer and
from another part to another synthesizer. Or you can send different ranges of keys to different
channels of a multitimbral synthesizer.
example
Link a Roland JV-1080 to your computer. On the JV-1080 setup a base sound on MIDI channel 0 and a
solo instrument on channel 1. Create a MIDI device link and link it to the JV-1080. Link your MIDI
keyboard to your computer. Create a MIDI device link and link it to your keyboard. Create a
Layer and split and let it get its input from the MIDI keyboard and send its output to
the JV-1080. Create a layer in the Layer and split for the keys below C4 and specify
channel 0. Create a layer for key C4 and all keys above, and set it up to send to channel 1. If you
now press C3 on your MIDI keyboard, you will hear a base sound coming from the JV-1080. If you press
C4, you will hear the solo instrument.
Lights
description
A Lights displays MIDI information in a frivolous way. Currently only playing notes are displayed.
A higher velocity yields a brighter colour. Note that this MidiInOut part has no output, only input.

typical use case
Use for diagnostic purposes to see if MIDI messages are flowing where you would expect them.
example
A Lights can typically be used for diagnostic purposes.
MIDI clock
description
A MIDI clock generates MIDI timing messages at intervals as specified by as beats-per-minute
(BPM) setting, as well as start, stop and continue messages.

typical use case
Use a MIDI clock to create MIDI clock messages (0xF8 or 248) for use by e.g. Echo and
Arpeggiator.
example
See typical use case above.
MIDI device link
description
A MIDI device link is a MidiInOut part that acts as a bridge between other MidiInOut parts and
other MIDI software and hardware devices. All MIDI drivers that have been selected in File |
Settings | system MIDI devices in the main m.nlcode.nl application window can be linked to.

typical use case
External hardware devices can be used via a MIDI device link.
example
Connect a MIDI keyboard to your computer. Enable its driver in File |
Settings | system MIDI devices. Create a MIDI device link and select the MIDI keyboard driver
from its dropdown. The messages generated by the external keyboard can now be used in m.nlcode.nl
by other MidiInOut parts.
MIDI message dump
description
A MIDI message dump is a MidiInOut part that displays all (or most) of all incoming MIDI messages.
When you set the write to file option, all new incoming messages will be written to file. The
file(s) can be found in the same directoy as the project file.
Note that this MidiInOut part has no output, only input.

typical use case
A MIDI message dump is typically used for diagnostic purposes.
example
Link a MIDI message dump to the outputs of a MIDI device link that is
linked to an external MIDI device to see which messages are send from that external device.
Note channel spreader
description
A Note channel spreader takes incoming notes from one specific MIDI channel and sends them in a
round-robin way via the specified MDI output channels. The first note goes to the channel with the
lowest number and which is selected for output. The second note goes to the second channel, etc.
If there are no more channels, the lowest channel will be used again. That way the incoming notes
are spread across the selected channels. Note off messsages will be sent to the same channel as
where its predecessing note on message has been sent.
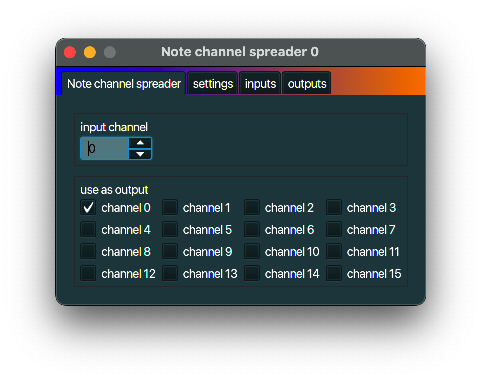

typical use case
If you have a number of the same type of mono synthesizer (or a number of the same type of
synthesizer with a limited number of voices) without support for poly chaining, you can use a
Note channel spreader to distribute notes over those synthesizers.
example
Link three Korg NTS-1 synthesizers to one MIDI hub. Assign each NTS-1 its own MIDI
channel, 0 through 2. Create a MIDI device link and link it to the driver of your MIDI hub.
Create a Note channel spreader and let it send its output to that MIDI device link. Select
channels 0, 1 and 2 for output. Create another MIDI device link, link it to an external MIDI
keyboard and make it send its output to the Note channel spreader. Play a three note chord on your
external MIDI keyboard. You will hear the notes from your chord simultaneuously from the three NTS-1
synthesizers.
Note gate (velocity)
description
A Note gate (velocity) acts as a gate in that it only sends out notes within certain velocity boundaries.
So basically you use a Note gate as a filter for notes that are too ‘soft’ or too ’loud’.
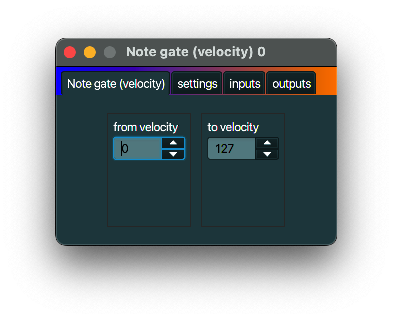

typical use case
Filtering notes based on their velocity.
example
No inspiration, sorry.
Note holder
description
A Note holder hold notes until those notes are played again. So instead of using a sustain pedal,
you can use a Note holder to keep a note playing after a note off message.
A Note holder can be handy when used together with an Arpeggiator MidiInOut part.
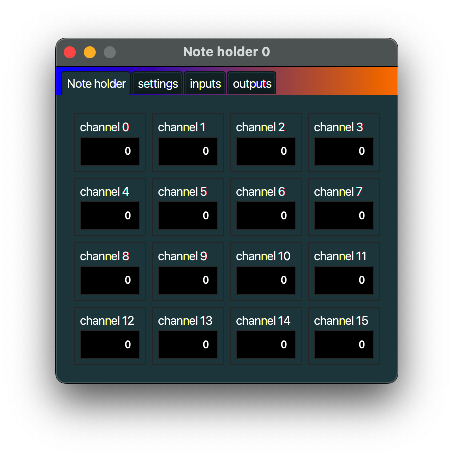

typical use case
Connect an Arpeggiator to the output of a Note holder to let the Arpeggiator
arpeggiate, while you have two hands free.
example
See typical use case above.
Program changer
description
A Program changer can select different patches, instruments, whatever you like to call it.
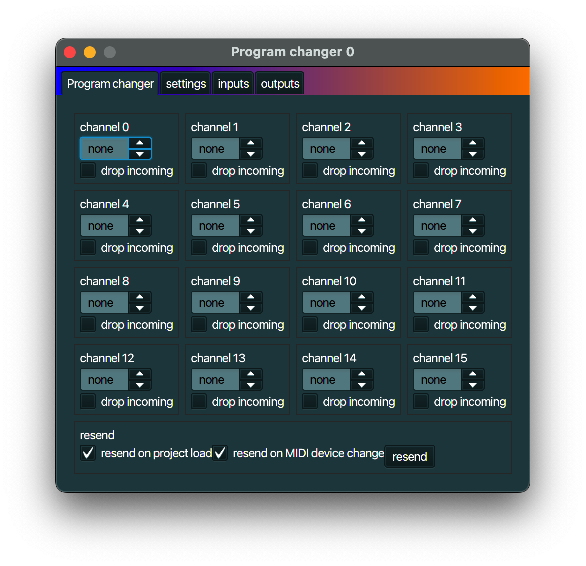

typical use case
Change the sounds that a synthesizer produces by changing the program.
example
Connect the outputs of a Program changer to the inputs of a
MIDI device link that is linked to a synthesizer. Play a note, select a
different program, and play the same note again. You hear a different sound.
Transposer
description
A Transposer transposes all note on and note off messages. It tries to be smart with note off messages if you changed the transpose height in between a note on and a note off.

typical use case
Generate sounds in the same key as that annoying guitarist is playing in, while playing the keys on your keyboard in a key you feel comfortable in.
example
Connect the outputs of a Transposer to the inputs of a
MIDI device link that is linked to a synthesizer. Connect the inputs of a Transposer to the outputs of a Keyboard MIDI Keyboard. Play a note, set the Transposer to transpose a semitone up, and play the same note again. You hear the sound a semitone higher.












